Vertically oriented 2D Model – Liedl et al. (2005)¶
This model, based on Liedl et al. (2005), provides an estimate of a steady-state plume length ($L_{max}$ ) from a vertically oriented 2D model domain (see figure). The vertical orientation refers to $z$-axis being aligned to the aquifer thickness.
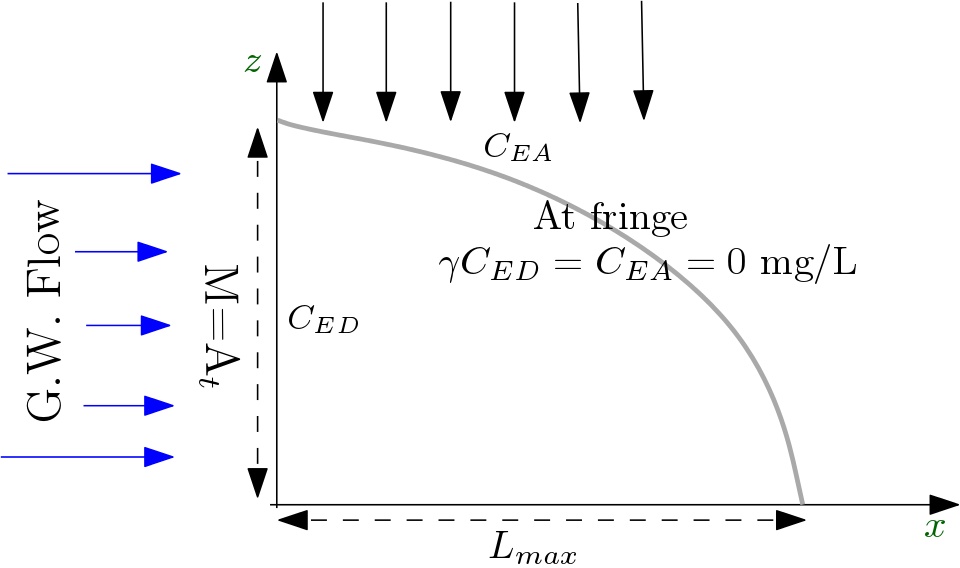
Liedl et al.(2005) provides the following explicit expression for $L_{max}$:
$$ L_{max} = \frac{4}{\pi^2}\frac{M^2}{\alpha_{Tv}}\ln\bigg(\frac{4}{\pi}\frac{\gamma C_{ED}^\circ + C_{EA}^\circ }{C_{EA}^\circ}\bigg) $$in which:
$M$ = Source Thickness [L], which is equal to Aquifer thickness ($A_t$) [L]
$\alpha_{Tv}$ = Vertical Transverse Dispersivity [L]
$\gamma$ = Reaction stoichiometric ratio [ ]
$C_{ED}^\circ$ = Contaminant (Electron Donor) concentration [ML$^{-1}$]
$C_{EA}^\circ$ = Partner Reactant (Electron Acceptor) concentration [ML$^{-1}$]
The model is based on the following assumptions:
- Steady-state condition in a homogeneous and isotropic aquifer.
- A single step bi-molecular instantaneous reaction between reactants taking place only at the fringe.
- The contaminant source (Electron Donor) penetrates entire thickness of the aquifer.
Reference:
Liedl, R., Valocchi, A., Dietrich, P., Grathwohl, P., 2005. Finiteness of steady state plumes. Water Resour. Res. 41, W12501. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005WR004000